Precious metals mainly refer to eight metal elements, such as gold, silver and platinum group metals (ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium and platinum). Most of these metals have beautiful colors, great resistance to chemicals, and inertness to chemical reactions under normal conditions.
With increasingly wide application of precious metals, the refining methods and technologies of precious metals are also getting well developed. At present, the dominant preparation method is Electrolysis-Electroplating Hydrometallurgy.
The process flow is as follows:
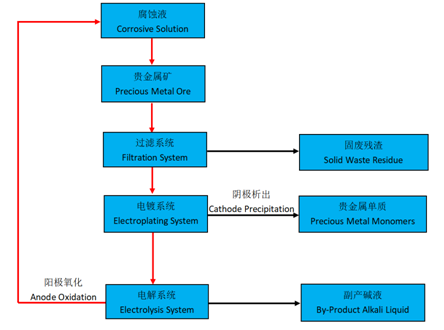
In the traditional process for precious metal gold production, aqua regia is used to corrode gold, and then gold is to be extracted from aqua regia corrosive solution. This process requires a series of sophisticated equipments. The operating conditions are complex and the safety risks are high.
Since bromine is easy to react with precious metals such as gold and platinum to form bromine salts, and the reaction process is mild, the risk is low, and the safety is controllable. Therefore, bromine corrosive solution is more and more popular in precious metal extraction. At present, the technological process of extracting gold by bromine corrosive solution is as follows: firstly, let bromine and bromine salt solution react with gold to form gold bromide solution; secondly, let the gold bromide solution pass through the electroplating system to precipitate high-purity gold on the Cathode and bromine on the Anode; finally, use the electroplating mixed liquid containing bromine as corrosion solution to extract gold again.
In the process of converting electroplating liquid to corrosion solution, an electrolytic membrane that only allows Cations to pass through is needed to accelerate the production of chlorine and bromine monomers. As the Cathode will produce a large number of hydroxyls and the Anode will produce a large number of oxidizing monomers, the membrane must have excellent chemical resistance to alkali and oxidation. The new electrolytic membrane developed by Guo Chu Technology perfectly meets the requirements of these two aspects.
Guo Chu Technology (Xiamen) Co., Ltd. has successfully developed an electrolytic membrane suitable for the Electrolysis System based on years of experience in membrane technology research and development, which can effectively increase the conversion rate of corrosive solution. At the same time, due to the lower membrane resistance compared with the traditional membrane, the overall energy consumption of the electrolysis system is also reduced.
The electrolytic membrane developed by
Guo Chu Technology (Xiamen) Co., Ltd. can withstand more than 3mol/l acid and alkali, and has smaller membrane resistance and requires lower voltage, which greatly reduces the energy consumption of electrolytic process. In addition, the electrolytic membrane is relatively dense, which has better retention effect on impurity ions and greatly improves the concentration and purity of by-product acid and alkali.
Guo Chu Technology (Xiamen) Co., Ltd., who is committed to the application and promotion of new membrane separation technology, with rich experiences in the application of special membranes in medicine, chemical industry, food, beverage, petroleum, petrochemical, nuclear energy and other industries, can develop membrane separation technology and equipment suitable for specific separation requirements according to the process requirements of customers.